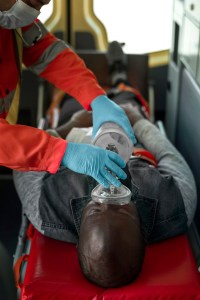
Minnesota’s Brain Injury (BI) Waiver Program has supported survivors of traumatic and acquired brain injuries since 1992. In 2026, it is facing sweeping changes, bringing both new benefits and serious concerns for tens of thousands of residents who depend on it.
On the positive side, the program covers 44 distinct services, has no waitlist, and swim lessons have been added as an allowable Consumer Directed Community Support expense. Administratively, “MnCHOICES is a computer application used… to support their assessment and support planning work for Minnesotans who need long-term services and supports (LTSS), regardless of age, type of disability or service needs.”
But disability advocates are alarmed. The 2025 Legislature passed $1.3 billion in disability waiver cuts, and structured day services – vital therapeutic programming for brain injury survivors – have been removed from the BI Waiver service definition entirely. Currently, roughly 15 to 20 states run standalone brain injury waivers, including Colorado, New York, Massachusetts, and Kansas, though they vary widely.
Additionally, recent investigation into the state’s BI Waiver Program, and into Medicaid grants, as a whole, seems to have also uncovered significant fraud, including overbilling for services, billing for services not rendered, and improper billing by unlicensed staff. In January 2026, this discovery of fraud prompted the state to freeze enrollment of the Brain Injury Waiver Program, and other programs.